|

Crohn's disease
Treatment plan for Crohn's disease
 Medications
available for Crohn's disease Medications
available for Crohn's disease
Here is
a general list of currently available medications used to treat Crohn's
disease, including how they work, when they might be used, and possible
considerations.
5-ASAs (5-aminosalicylic acid)
This type of medicine may be used to help reduce inflammation. It is
usually used for mild to moderate symptoms. It is useful for the
induction of remission (to help lessen symptoms and restore health), but
is not useful for maintaining remission (keeping your symptoms from
returning). It may take 4-8 weeks before you start to feel relief of
symptoms.
5-ASAs
are usually taken daily, either orally or rectally (as an enema or
suppository). They are considered a safe treatment option when used
long-term.
Examples of 5-ASAs include: mesalamine, balsalazide, olsalazine and
sulfasalazine.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are also used to help reduce inflammation in Crohn's
disease. They can be effective for induction of remission (to help
lessen symptoms and restore health) in moderate and severe Crohn's
disease. They are not, however, meant to be used long-term due to the
associated side effects.
Corticosteroids may start relieving symptoms within 1-3 weeks. In some
cases, remission may be reached within 6-8 weeks.
Usually your doctor will want to re-evaluate you in 2-3 weeks after you
have started taking corticosteroids, to see how you are doing and
whether you are having any response to the medicine or if you are having
any problems.
Steroids are taken intravenously, orally or rectally (eg, an enema). The
most commonly reported side effect is infection. Other related problems
include bone mineral loss (which may be managed with supplements of
calcium and vitamin D), slowing of growth in children, increased
appetite, weight gain, disturbed sleep pattern, a so-called 'moon-shaped
face' due to fluid retention in the skin (called Cushing's syndrome), or
acne.
Examples of corticosteroids include: prednisone, methyl prednisolone and
hydrocortisone.
For
disease at the end of the small intestine, or right side of the colon,
budesonide (a glucocorticosteroid drug) may be used and is considered to
have fewer safety concerns.
Immunosuppressants
Two-thirds of people with IBD will take an immunosuppressant at some
point. These medicines keep down inflammation by suppressing (lessening)
the activity of the immune system.
Immunosuppressants are used to maintain remission (keep symptoms from
returning) and are 'steroid-sparing', meaning they can help reduce the
dose of corticosteroids needed. They are often used to treat moderate to
severe Crohn's disease.
Immunosuppressants take a while to start working (approximately 2-4
months), so they are often taken along with corticosteroids. They are
either taken orally (thiopurines such as azathioprine or
6-mercaptopurine, also known as 6-MP) or as injections (methotrexate).
It is
important to keep taking your medication, as there are good benefits.
However, some people may have to stop because of side effects. It is
important to discuss this with your doctor first. These may include:
nausea, myelosuppression (lowering the bone marrow's ability to make
blood cells, which can require frequent blood tests) or risk of
infection such as viral herpes (eg, cold sores). Thiopurines also have a
risk of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). Treatment with
azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine may also bring about a slight increased
risk of lymphoma (cancer of the lymphatic system). Regular monitoring,
therefore, is essential.
If you
have any of these problems, or any other symptoms while taking this
medicine, contact your doctor right away. Your doctor will also probably
want to monitor you regularly while you are taking this medicine.
Examples of immunosuppresants include: azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine
(6-MP) and methotrexate.
Anti-TNFα
Current anti-TNF drugs are biologic therapies, meaning that the drugs -
antibodies or receptors - are produced by living cells. They are used
for moderate to severe Crohn's disease. They can work quickly (generally
within 2-4 weeks) and can be effective in people with inflammation
limited to the gut wall and also if you have a fistula. They may also be
used in people in whom other treatments haven't worked well.
Anti-TNFs can be taken either as injections (administered at home) or
through a drip (given in the hospital).
Before
taking this medicine, your doctor will ask to screen you for
tuberculosis with a chest X-ray and/or a skin test. There is a risk of
infection, although it is lower than that associated with steroid use.
There may also be allergic reactions such as joint pain, rash, or a
short-term (transient) reaction or fever. Other potential safety
concerns include heart failure in the elderly (watch for swollen ankles
or shortness of breath) or skin disorders.
If you
are taking anti-TNF medicine and experience any symptoms such as night
sweats, cough or shortness of breath, contact your healthcare
professional.
There
have been rare reports of cancers associated with biological therapy,
but it is not yet known whether these were due to these medicines or to
other medication given at the same time. Research is ongoing to look at
both possibilities.
Examples of anti-TNFs (in Europe) include: infliximab and adalimumab.
Medical
devices
Apheresis
(leukocytapheresis)
Cells of
the immune system called white blood cells (or leukocytes) defend the
body against infections. In people with active IBD types of leukocytes
called granulocytes and monocytes are often increased or over active.
Large numbers of these cells enter the wall of the intestines and can
release substances that cause bowel injury and stimulate inflammation.
It is believed that the watery diarrhoea seen in severe IBD is a result
of injury to the absorptive epithelium which makes it unable to absorb
water.
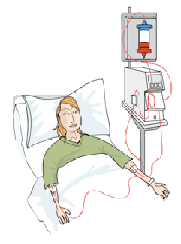 Apheresis, or leukocytapheresis, is performed with a medical
device that selectively binds excess or activated granulocytes and
monocytes from the blood. Blood is pumped from a vein in one arm (via a
simple venopuncture) through a column containing cellulose acetate beads
or a filter. This binds granulocytes and monocytes while the rest of the
blood passes right through and is infused back into the body through the
other arm. The outcome is a reduction in the number of inflammatory
cells that can move from the blood into the intestinal wall. As a
result, the symptoms of IBD are relieved, and the bowel gets a chance to
heal. Apheresis, or leukocytapheresis, is performed with a medical
device that selectively binds excess or activated granulocytes and
monocytes from the blood. Blood is pumped from a vein in one arm (via a
simple venopuncture) through a column containing cellulose acetate beads
or a filter. This binds granulocytes and monocytes while the rest of the
blood passes right through and is infused back into the body through the
other arm. The outcome is a reduction in the number of inflammatory
cells that can move from the blood into the intestinal wall. As a
result, the symptoms of IBD are relieved, and the bowel gets a chance to
heal.
The
treatment lasts for 1 hour and is usually given once a week for 5 weeks.
It can be performed in hospital or in an outpatient setting.
Leukocytapheresis
involves mainly adults with IBD - there is some debate as to whether it
is suitable for children. It can be used to reduce symptoms during a
severe flare up, or in moderate to severe active IBD in which
satisfactory effects have not been achieved with corticosteroids or
other immunosuppressive therapy.
Some
temporary side effects can occur, such as low blood pressure,
palpitations, and hot flushes; however, little is known about the
long-term side effects of apheresis.
The
biological processes through which leukocytapheresis affects the course
of disease remain largely unknown, and it is difficult to draw
conclusions from the existing clinical trial data on how effective the
treatment really is.
|



